2024-future
September
Trace history, embark on the journey of today. Let the union of antiquity and creativity beautify our intellectual landscape.
19th Century to Contemporary (1830 CE – Present):
September

Historical and Political Themes. Symmetry and Order.
Symmetry and Order.
Historical and Political Themes. Symmetry and Order.
.Modern Period (1800 CE – 1950s):
Realism and Impressionism:
The 19th century saw a shift towards realism, depicting contemporary life with accuracy and detail. Sculptors like Auguste Rodin broke away from traditional styles, embracing more expressive and dynamic forms.
Impressionist influences led to a focus on capturing the play of light and movement in sculptures. Rodin’s “The Thinker” and “The Kiss” exemplify this departure from conventional representation.
Avant-Garde Movements:
The early 20th century witnessed avant-garde movements like Cubism, Futurism, and Surrealism challenging traditional norms. Artists like Pablo Picasso and Salvador Dalí experimented with abstract and fantastical forms, influencing sculpture with unconventional shapes and materials.
.Contemporary Period (1950s – Present):
Abstract Expressionism:
Post-World War II, Abstract Expressionism emerged, emphasizing spontaneity and emotional expression. Artists like Jackson Pollock extended the concept of abstraction to sculpture, creating non-representational and emotionally charged works.
Minimalism and Conceptual Art:
The 1960s saw the rise of Minimalism, characterized by simplicity, geometric shapes, and a focus on materiality. Artists like Donald Judd and Dan Flavin explored the intrinsic qualities of materials in their sculptures.
Concurrently, Conceptual Art questioned the traditional notions of art, with artists like Joseph Kosuth and Sol LeWitt emphasizing the idea or concept behind the artwork rather than its physical form.
Postmodernism and Eclecticism:
Postmodernism in sculpture, starting in the late 20th century, embraced eclecticism and a rejection of rigid categorizations. Artists combined diverse styles, materials, and cultural references, questioning the idea of a single, linear narrative in art.
Installation and Environmental Art:
Contemporary sculpture expanded beyond traditional gallery spaces. Installation and environmental art became prominent, with artists like Christo and Jeanne-Claude creating large-scale, site-specific works that engaged with the surrounding environment.
Technology and Digital Art:
The 21st century introduced technology and digital elements into sculpture. Artists incorporated 3D printing, interactive elements, and digital projections, exploring the intersection of traditional craftsmanship with modern technology.
September
Classical aesthetics influenced not only sculpture but also architecture, painting, and other art forms during this period.
.Baroque Period (1600 CE – 1750 CE):
Dramatic Expression:
Baroque sculpture embraced drama, emotion, and grandeur. Artists aimed to evoke strong emotional responses through dynamic poses, intense facial expressions, and elaborate details.
Gian Lorenzo Bernini, a prominent Baroque sculptor, created masterpieces like “Ecstasy of Saint Teresa” and “David,” showcasing a theatrical and emotional approach.
Architectural Integration:
Baroque sculptures often became integral parts of architectural ensembles. They adorned grand fountains, churches, and public spaces, contributing to the overall decorative scheme of the Baroque period.
Theatricality extended to architectural features, with sculptures seamlessly blending with the surrounding structures.
.Rococo Period (18th century):
Delicate Elegance:
Rococo sculpture emerged as a reaction to the grandeur of the Baroque. It favored delicate forms, intricate details, and a more lighthearted, playful aesthetic.
Sculptures during this period often depicted graceful figures, love themes, and pastoral scenes, reflecting the Rococo emphasis on beauty and charm.
.Neoclassical Period (late 18th century – early 19th century):
Return to Classicism:
Neoclassicism marked a return to the classical ideals of ancient Greece and Rome. Artists sought inspiration in the simplicity, symmetry, and order of classical art.
Antonio Canova, a prominent Neoclassical sculptor, created works like “Psyche Revived by Cupid’s Kiss,” embodying grace, harmony, and a focus on idealized beauty.
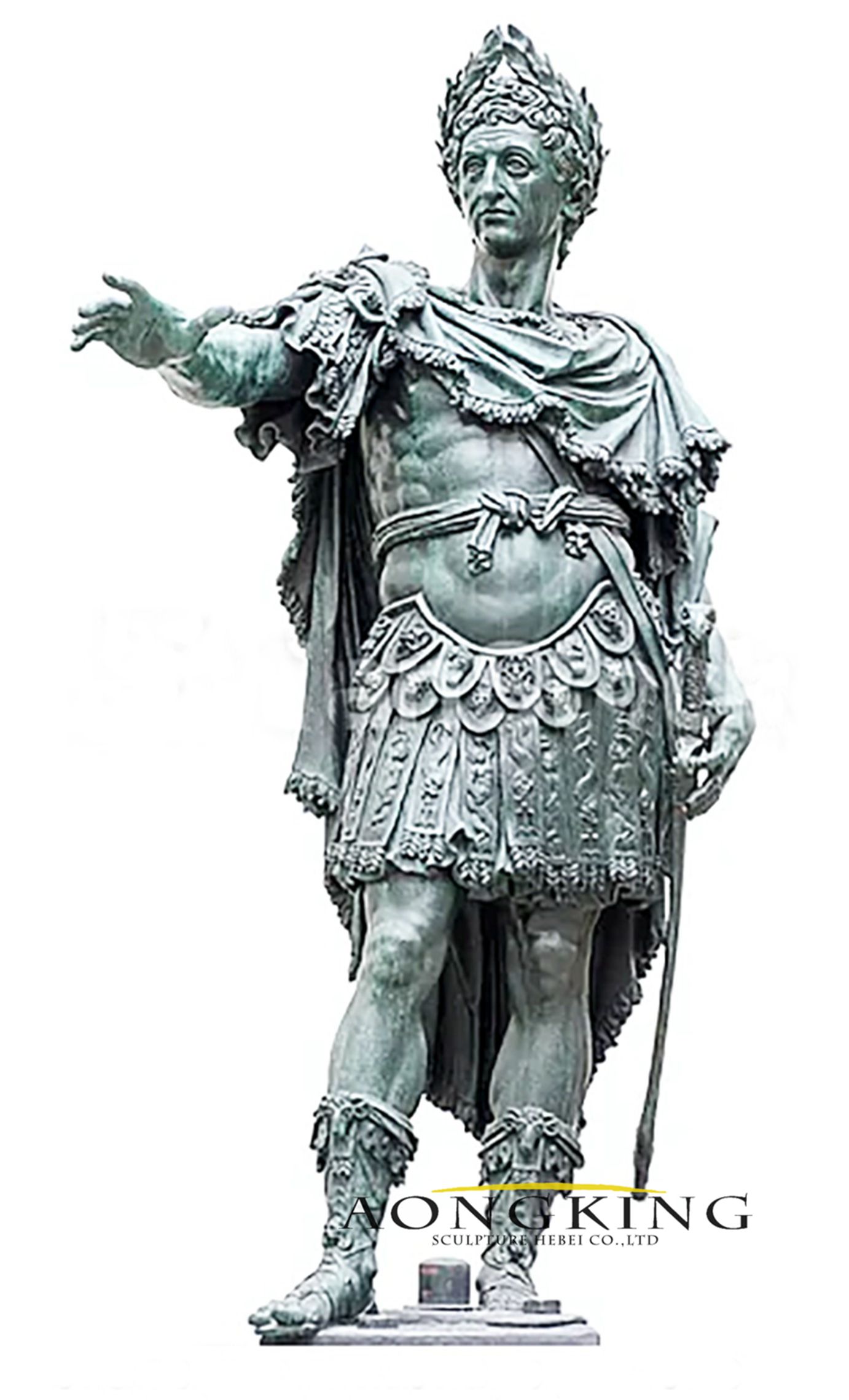
Historical and Political Themes:
Neoclassical sculpture often portrayed historical or mythological figures as well as political leaders. Sculptors aimed to convey moral virtues, civic duty, and the spirit of the Enlightenment.
Jean-Antoine Houdon’s portrait sculptures, including the famous bust of Voltaire, exemplified the Neoclassical emphasis on intellectual and political ideals.
Symmetry and Order:
Neoclassical sculptures emphasized clear lines, geometric forms, and a sense of proportion. The focus on rationality and order reflected the intellectual climate of the Enlightenment.
The shift toward classical aesthetics influenced not only sculpture but also architecture, painting, and other art forms during this period.
Middle Ages to Renaissance (476 CE – 1600 CE):
June
The Renaissance marked a significant shift towards humanism, scientific inquiry, and artistic innovation.
Sculpture became a medium for expressing individualism, emotion, and the exploration of the human form.
.Medieval Period (1000 CE – 1400 CE):
Romanesque Sculpture (1000 CE – 1200 CE):
Characterized by sturdy, simplistic forms, Romanesque sculpture adorned churches and monasteries. Subjects often included biblical figures and scenes, serving didactic purposes for the largely illiterate population.
Sculptures were integrated into architectural elements, such as doorways and capitals, showcasing a fusion of art and religious architecture.
Gothic Sculpture (12th century – 16th century):
Emerged with the Gothic architectural style, emphasizing height and light. Gothic sculptures adorned cathedrals with intricate detailing and expressive features.
Statues of saints, biblical narratives, and grotesque figures embellished the exteriors and interiors of Gothic structures, portraying a sense of divine transcendence.
.Renaissance Period (14th century – 17th century):
Early Renaissance (14th century – 16th century):
Marked by a revival of classical ideals, artists sought inspiration from ancient Greek and Roman art. Sculptors like Donatello introduced naturalism and perspective, emphasizing anatomical accuracy.
Biblical and mythological themes remained popular but with a newfound emphasis on realism and emotional expression. Notable works include Donatello’s “David.”
High Renaissance (late 15th century – early 16th century):
The pinnacle of Renaissance art is characterized by the works of Michelangelo, Leonardo da Vinci, and Raphael. Sculptures achieved unprecedented levels of technical skill, embodying harmony, proportion, and idealized beauty. Michelangelo’s “David” and “Pieta” exemplify the perfection of form, while his monumental project, the Sistine Chapel ceiling, showcases mastery in fresco painting.
Mannerism (late 16th century):
Reacting against the harmonious ideals of the High Renaissance, Mannerism introduced distortion and exaggeration in form. Sculptures displayed elongated proportions and unconventional poses, evoking a sense of tension and instability.
Classical Antiquity (500 BCE – 476 CE):
December

Legacy and Influence:
Classical ideals of balance, harmony, and naturalism in sculpture
The classical ideals of balance, harmony, and naturalism in sculpture laid the foundation for Western art for centuries to come.
Roman sculptures, in particular, had a lasting impact on portraiture and monumental art, influencing the Renaissance and later artistic movements.
.Greek Sculpture (500 BCE – 323 BCE):
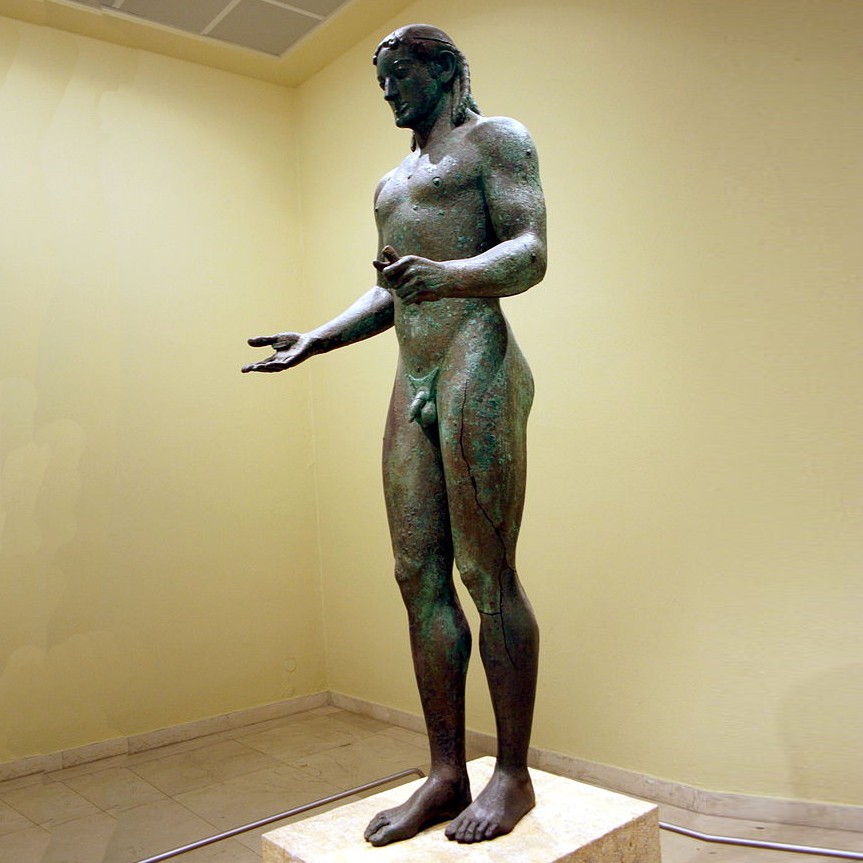
Archaic Period (500 BCE – 480 BCE):
Characterized by the emergence of rigid, stylized forms, Archaic Greek sculptures often depicted idealized figures with a smile known as the “Archaic smile.” Kouros and Kore statues marked this period, displaying a progression towards more naturalistic proportions.
Classical Period (480 BCE – 323 BCE):
The epitome of Greek sculpture, this era produced iconic works reflecting ideal beauty and realism. Polykleitos’ “Doryphoros” exemplifies the pursuit of perfect proportions, while the Parthenon sculptures showcase the harmonious integration of architecture and sculpture in monumental contexts.
.Hellenistic Sculpture (323 BCE – 31 BCE):
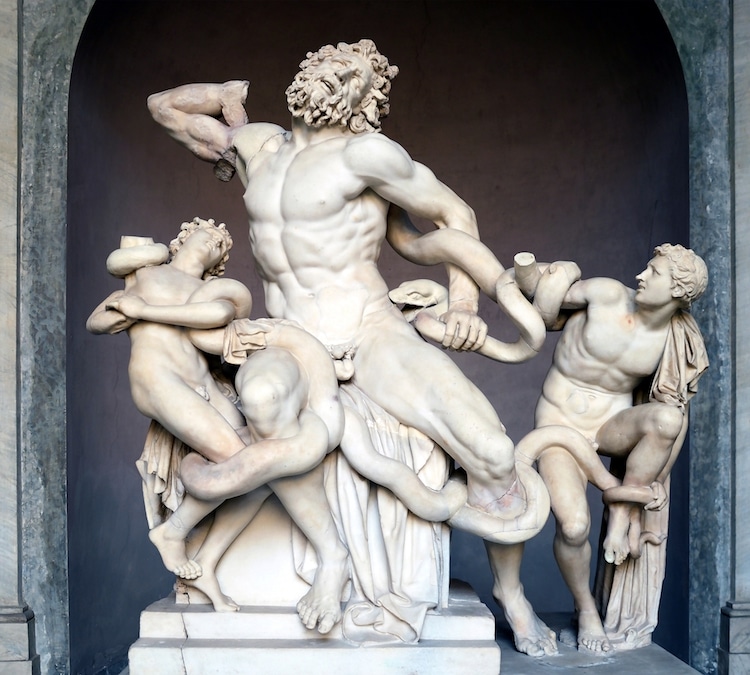
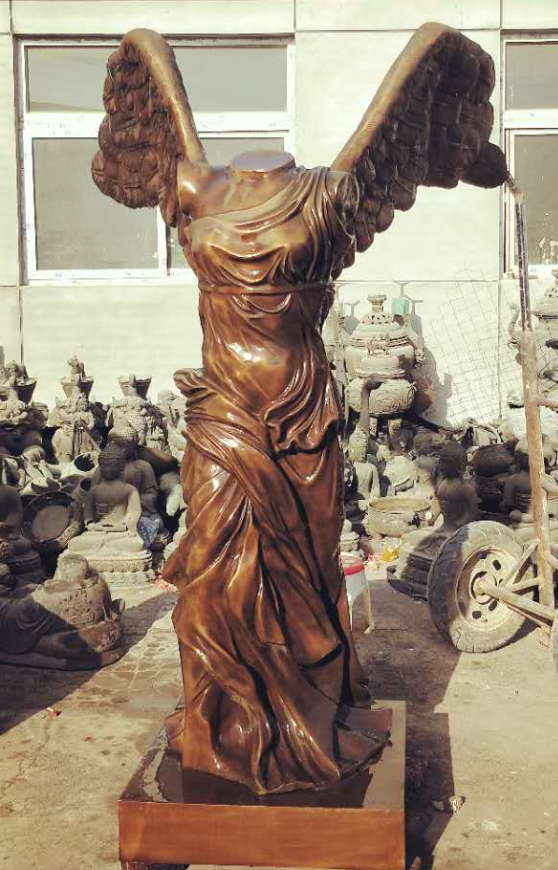
Hellenistic Expansion: Following the conquests of Alexander the Great, Greek influence spread throughout the known world. Hellenistic sculptures embraced emotion, dynamic poses, and a wide range of subjects. The “Laocoon and His Sons” and the “Nike of Samothrace” exemplify the dramatic and expressive qualities of this period.
.Roman Sculpture (509 BCE – 476 CE):
Republican Period (509 BCE – 27 BCE):
Early Roman sculptures were influenced by Etruscan and Greek styles, often focusing on historical and political themes. Portraiture became prominent, capturing the likenesses of political figures and notable citizens.
Imperial Period (27 BCE – 476 CE):
Roman sculpture flourished during the reign of Augustus and subsequent emperors. Portraiture continued to be significant, showcasing individualized realism. Architectural reliefs, triumphal arches, and colossal statues celebrated military victories and imperial power.
December

So far discovered, the origin of civilization, the emergence of sculpture
The emergence of sculpture
So far discovered, the origin of civilization, the emergence of sculpture
1, The “Sanxingdui” site is hailed as one of the greatest archaeological discoveries of the 20th century, revealing that, like the Yellow River basin, the Yangtze River basin is part of the cradle of Chinese civilization. It is often called “the ‘source of the Yangtze Civilization”.
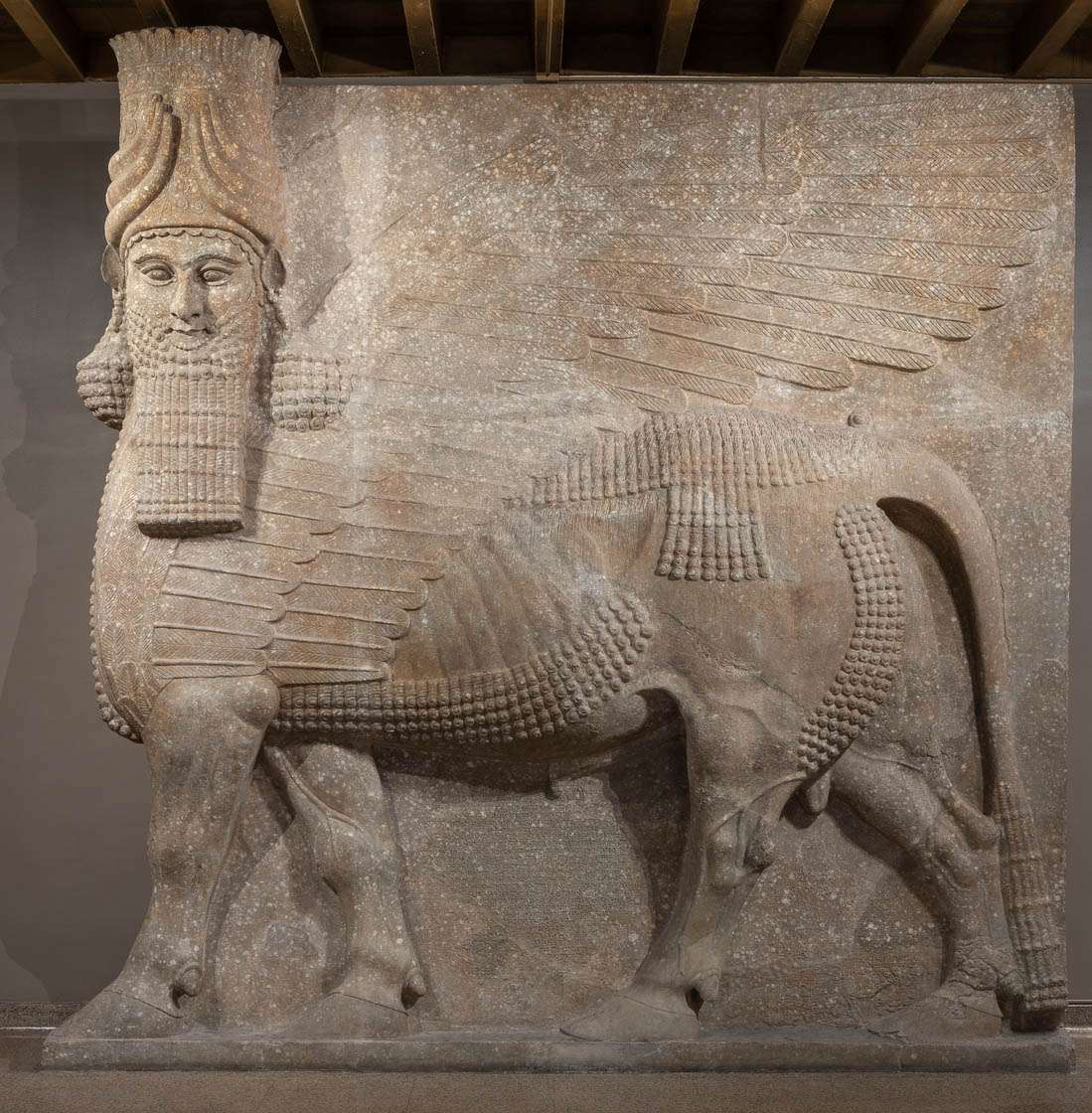
2, “Mesopotamian Sculpture” During this period, civilizations like Sumeria and Babylon produced intricate sculptures, often depicting deities and rulers.
3, “Egyptian Sculpture” is Notable for monumental works like the Great Sphinx and the statues of pharaohs, emphasizing the afterlife and divine representation.
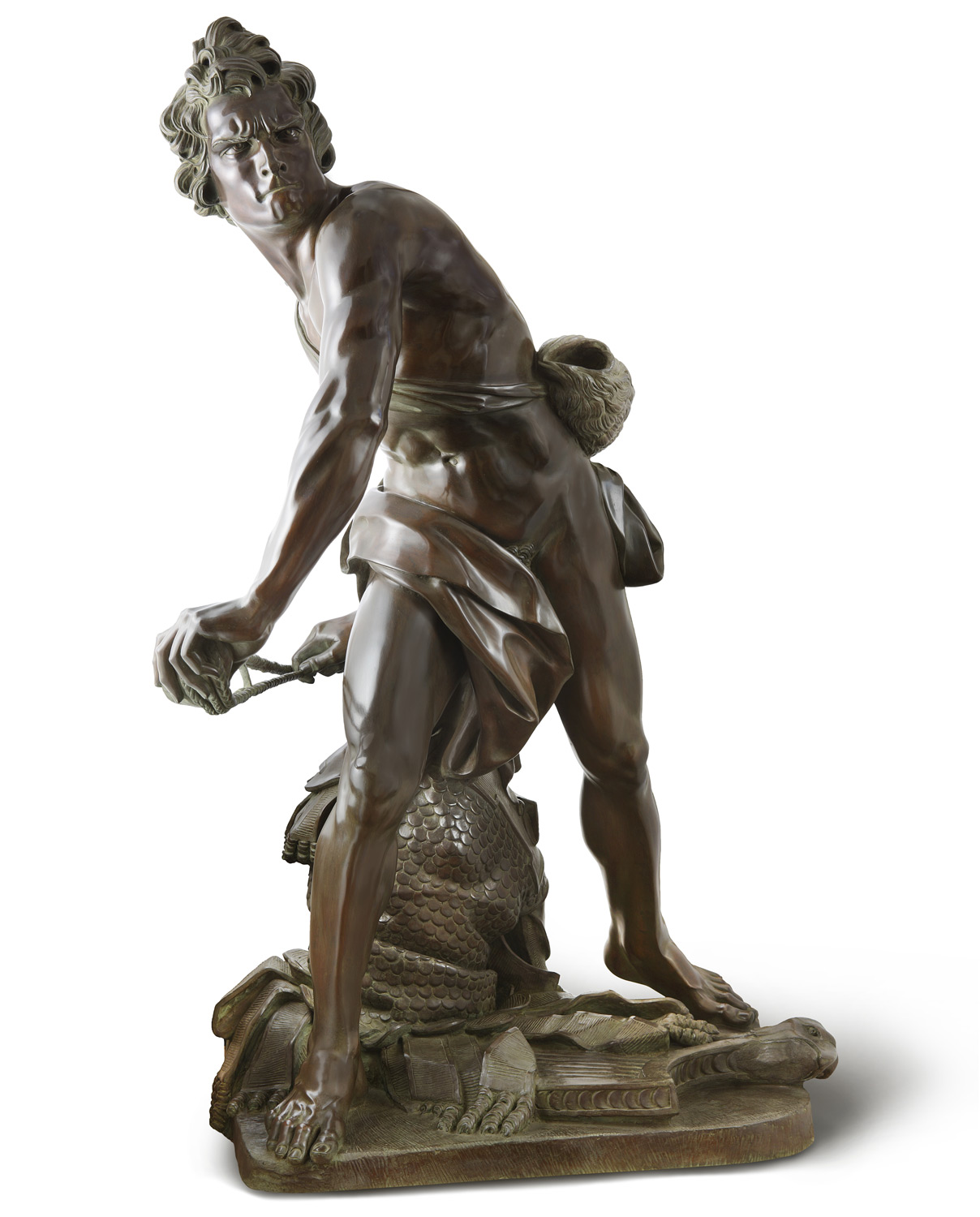
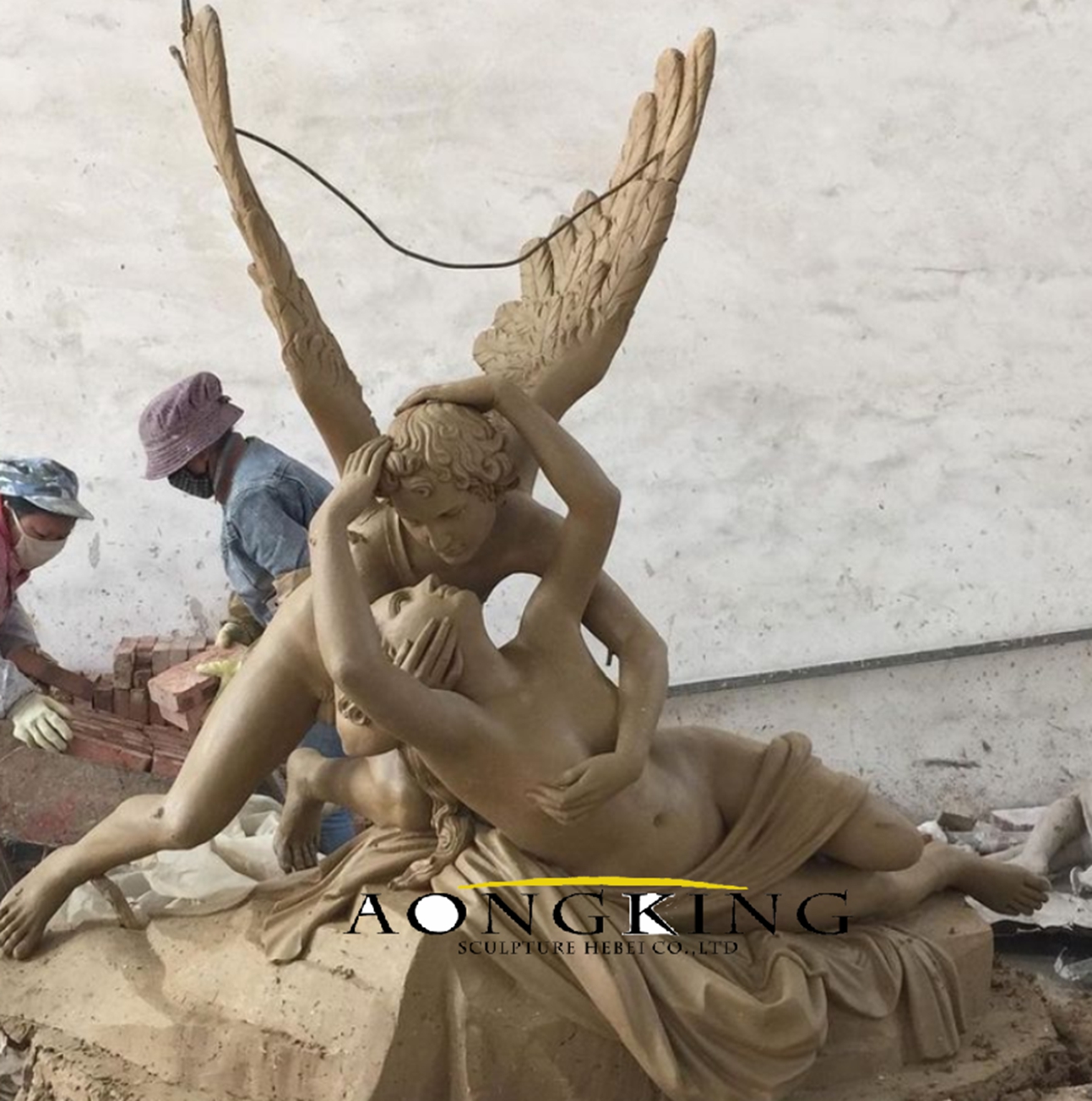
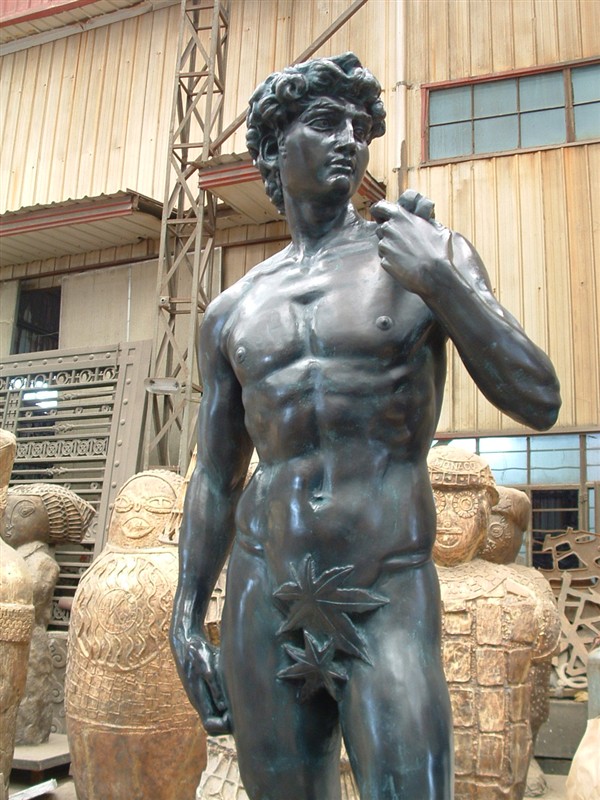
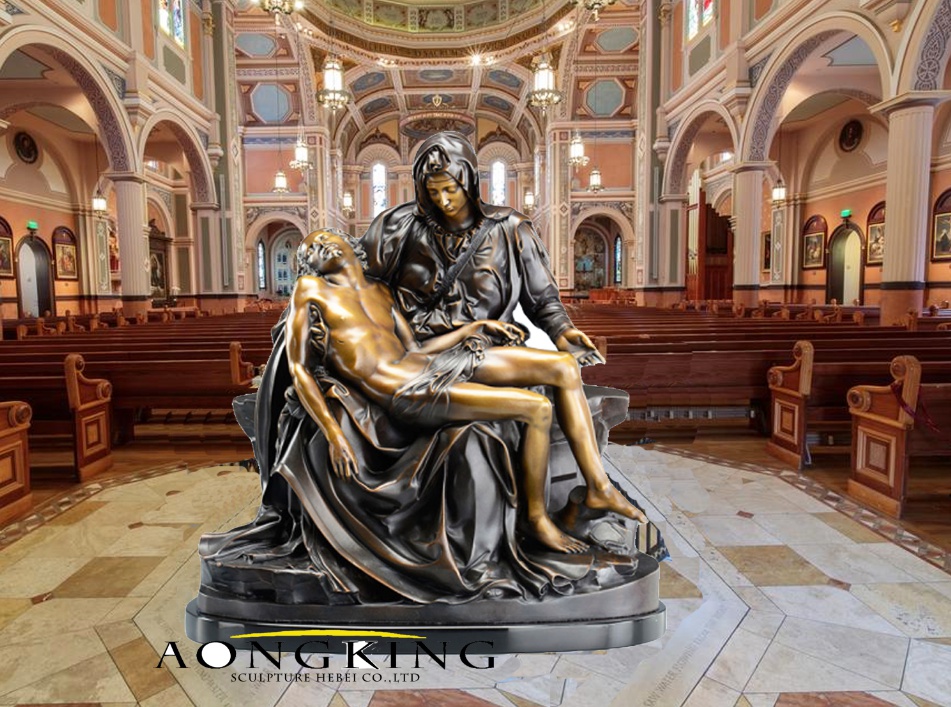

































Leave A Comment